C o u n t L i n e s o f C o d e
-
In order to assess, manage and optimize software development projects, 'code measuring' tools are required. A basic functionality consists in simply counting all lines of code - which I propose to do next. If the source is coded in clearly separated modules (adaptable, reusable), one may later extend the analysis to sophisticated parameters possibly leading to in depth code evaluation (according to predefined guide lines).
Project 'count lines' divides in two steps:
The first step consists in analyzing single source files (directly entered by the user in the command line). The resulting program is called CountLines_1x (versions 1.x).
-
In most real cases however, users do not intend to perform the analysis on single files. Rather they need results pertaining to a complete project stored within a few directories.
Actually, we already dispose of a code basis for searching file names matching defined patterns in one or several directories: List_Dir_1_2 (or later) (implementing a recursive search algorithm). A good opportunity to reuse it!We propose to develop the final program CountLines_2x (versions 2.x) by merging the code basis of List_Dir_1_2 (or later) and CountLines_1x.
To reuse the existing code basis it was necessary to enhance its degree of modularity. Procedures have been partitioned into separated module files .pm leading to following versions: List_Dir_1_3.pl (and modules), CountLines_1_3.pl (and modules).
The reuse of a well structured code basis has major advantages:
- It is a garant for readability and adaptability of the code.
- It shortens expenses for code verification and validation, provided that existing procedures have already been tested.
The price is a carefully designed code architecture - which should always be the case, especially if reuse is an option.
-
-
The flow chart below shows the last implemented 1.x version. It identifies procedures linked to the represented treatment steps.
One major difference to the initial concept (version 1.0) is that CountLines.pl, from version 1.2 on, does not focus anymore on a single language - say either CountLines_Perl.pl or CountLines_Perl_C.pl. Rather it will process any (existing) file, provided that its name matches a pattern identifying a supported language e.g. Perl.
- In many projects, coding languages are mixed e.g. embedded code will mostly be written in C but part of the preprocessing, may be performed by Perl or Python sources e.g. if "private" variables or complicated macros need be separately documented.In order to reach this flexibility, the decision whether to process a single file is taken at last - as a file is extracted from the treatment queue. Still, code maintainability requires that each language be processed in separate procedures, all supporting identical interfaces (input, output).
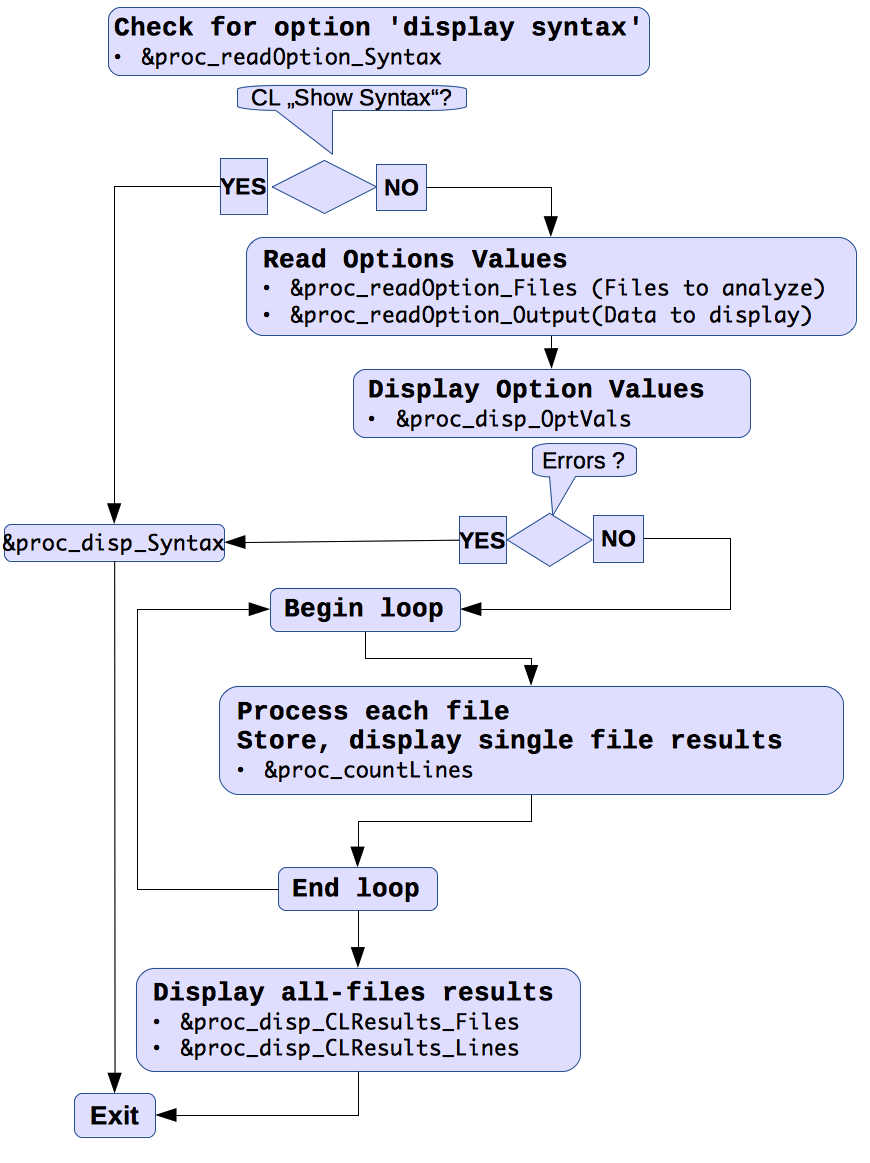
Fig.: Flow chart of CountLines_1_3.pl (version 1.3) -
Command line options follow following scheme option=value.
Tab. Command Line Options of CountLines_1_2.pl (or later) Remarks:Option Value Signification -syn Option show_syntax
If set, perl CountLines_1_2.pl will only display a list of available options and legal values then exit.-Fil FileName1[,FileName2[,..]] Option file list
contains a list of files the user wants to be processed.There may be one or several lists of files, each file in one list separated by a comma (,) or semi-column (;). All names are immediately checked - and rejected, if the corresponding file cannot be retrieved.
If no existing file has been extracted from the initial user list, treatment is aborted.
-Out {0, 1, 21, 22, 23, 2} Option display data
controls the amount of (debugging) data or results to display.0 display a minimum amount of information e.g. errors, warnings (default value) 1 In addition to 0, display CountLines results for each file successful processed 21 Debugging output: In addition to 1, display code lines of each file 22 Debugging output: In addition to 1, display comment lines of each file 23 Debugging output: In addition to 1, display code lines containing only { or } or {} - as meaningful symbols. 2 Debugging output is equivalent to 21, 22 and 23 - As the case for most programs presented, flexibility is tolerated to a certain degree with respect to the command line e.g. -Fil=AFileName or -file=AFileName, FILE=AFileName are equally accepted.
- Display option values -out= 21 | 22 | 23| 2 should only be used for debugging purposes, since the amount of data displayed is large.
-
A series of tests has been conducted to assess the behavior of versions 1.1. The following use case show only the quintessence: A list of files containing only one Perl and one C file.
perl countLines_1_2.pl -fil=countLines_1_2.pl,DeleteTree.c out=1 > results.txt
The result stored in results.txt is following:
countLines_1_2.pl begins Fr 13 Nov 2015 19:36:45 CET ### Command line [countLines_1_2.pl -fil=countLines_1_2.pl,DeleteTree.c out=1] Option -fil List of [ 2] file(s) to treat - 1- [countLines_1_2.pl] - 2- [DeleteTree.c] Option -out displays standard results for each file File [ 1] [countLines_1_2.pl] 1 Total number of lines [ 968] [= 100.00 percent] 2 - Number of coding lines [ 632] [= 65.29 percent] 3 + Number of code lines containing only alphanumerics '{' or '}' or '{}' [ 54] [= 5.58 percent] 4 - Number of commenting lines [ 220] [= 22.73 percent] 5 Number of empty lines (no alphanumerics at all) [ 116] [= 11.98 percent] Check sum = 1 - (2+4+5) (should be equal to zero) [ 0] File [ 2] [DeleteTree.c] 1 Total number of lines [ 258] [= 100.00 percent] 2 - Number of coding lines [ 162] [= 62.79 percent] 3 + Number of code lines containing only alphanumerics '{' or '}' or '{}' [ 17] [= 6.59 percent] 4 - Number of commenting lines [ 50] [= 19.38 percent] 5 - Number of empty lines (no alphanumerics at all) [ 46] [= 17.83 percent] Check sum = 1 - (2+4+5) (should be equal to zero) [ 0] General overview [ 2] files proposed for treatment [ 2] files actually treated 1 Total number of lines [ 1226] [= 100.00 percent] 2 - Number of coding lines [ 794] [= 64.76 percent] 3 + Number of code lines containing only alphanumerics '{' or '}' or '{}' [ 71] [= 5.79 percent] 4 - Number of commenting lines [ 270] [= 22.02 percent] 5 - Number of empty lines (no alphanumerics at all) [ 162] [= 13.21 percent] Check sum = 1 - (2+4+5) (should be equal to zero) [ 0] Total duration of process 0.03 Sec countLines_1_2.pl ends Fr 13 Nov 2015 19:36:45 CET In the use case, countLines_1_2.pl analyzes its own coding. The Zip-Archive available for download will therefore only contain the Perl source file itself. (The C-file used, DeleteTree.c, is not yet released for publication.)
-
-
-
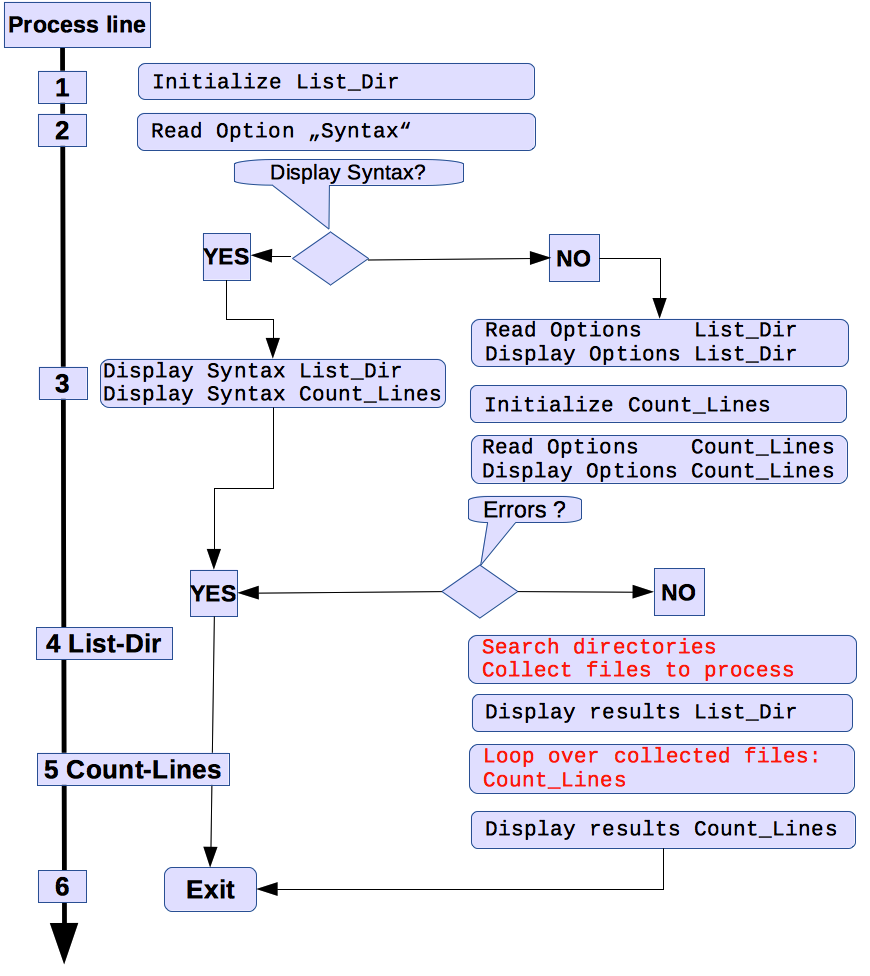
Fig.: Flow chart of CountLines_2_2.pl (version 2.2)In Version 2.2 and later, the CountLines.pl source code has been merged out of List_Dir_1_2 and CountLines_1x. A deliberate effort has been made to reuse the existing code basis as is. To fulfill this condition, both List_Dir.pl (version 1.3) and CountLines.pl (version 1.3) have been refactored.
-
Theoretically, the command line options set for CountLines_2_2.pl (or later) is the union of both command line option sets for List_Dir_1_2 and CountLines_1x, except for a few restrictions.
Tab. Restrictions regarding Command Line Options of CountLines_2_2.plModule Option=Value Restriction List-Dir -ScoDis Option Display Scope protocolling the project directories search is deactivated
(i.e. its value is set to zero, without possibility to change it).Count-Lines -Fil Option file list is meaningless (deactivated), since files to process are extracted from the project directories specified in option -ListDir.
The user may set all other option values, either by entering option=value in the command line directly or by naming a so called option file that lists those values, see option -OpFil (An example of option file can be found in the download archive).
Except for a few exceptions, only 2 options should be set:
-
CountLines_2_2.pl has been used to calculate the Lines Of Code (LOC) for all Perl projects published so far, see following LOC tables: Numerical Projects, IT Projects.
-
-
Following ZIP-Archives - Perl code, use case - are available for download from the Perl Project Sources table:
Tab. Download CountLines Archives (Perl sources, Option file)No. Download Refs Short Description 1 CountLines_1x Version 1x processes single source files - as listed in command line option(s) -fil. Following languages are currently supported: Perl, C.
Keywords Count lines of Code, Code Analysis Doc see CountLines_1x 2 CountLines_2x Version 2x: Recommended for practical use. In most real cases, users do not want to analyze a few files, but all files pertaining to a project, usually stored within a few directories. Following languages are currently supported: Perl, C.
Keywords Recursive tree-search, Counting Lines of Code Doc see CountLines_2x